Data archiving is storing data in a format that’s easily accessible, safe, and secure.
There are many different storage mediums and methods of data archiving, not to mention hundreds of data archiving solutions on the market, and it can be daunting to choose the right ones.
Luckily, there are a few best practices and tips you can follow to ensure that your data archiving strategy (and data archiving solution) suits your business requirements. Let’s dig into a few.
Why is Data Archiving Important?
Data archiving is important because it allows organizations to keep track of their data and ensure that it is not lost or corrupted.
Your data archiving policy will ensure that you keep the files you need according to regulatory compliance requirements, like GDPR or HIPAA regulations, while ensuring that your archived data isn’t taking up unnecessary (and costly) server space.
Your data archiving software can also form an important part of your data backup strategy, ensuring smooth and seamless data retention that can restore your vital data in the event of a data breach, inadvertent data losses due to disk failures or human error, or any other data loss.
Data archiving can also help organizations save money by reducing the need to purchase new long term storage devices.
What Types Of Data Can Be Archived?
It’s important to note that not all types of data can be archived, and vice versa.
For example, textual data like blog posts and social media messages can’t be kept in archive storage because they can’t be scanned digitally.
However, the opposite is also true; numerical data like stock prices and sales figures can be archived because they are easy to store on a computer and can be analyzed using software tools.
The key is finding a balance between the amount of data and the type of data you want to archive.
When Should You Archive Data?
There are several good reasons to archive data, but you need to consider when this data will be most helpful before deciding to store it.
Archiving data that is not required frequently results in wasted space and extra work to access it when needed.
In addition, it is generally a good idea to archive data that is older than you currently need because it is likely that you will need it at some point in the future.
Conversely, data that is still relevant today can be left in place and re-analyzed when required.
What Should You Keep In Mind While Archiving Data?
It will help if you keep several things in mind while archiving data, ensuring that it can be readily accessed when needed.
For example, if you need more rights to view, analyze, or print the data, you may keep a partially unusable copy that you cannot share.
In addition, when possible, ensure that the archived data is backed up frequently and stored safely.
Archiving data is crucial in analyzing and wrangling large quantities of data.
You should also note that it can be challenging to determine when to archive data and to which type of data, so it is important to follow a few basic guidelines and have a data archiving plan in place to make sure that you’re retaining the right information.
Best Methods to Archive Data in 2023
- Multi-Cloud Storage
- Create Your Own Data Lake
- Cloud Archiving Services
- Tape Archiving
- On-site Backups
- Network Storage
- Optical Disk Archiving
- Magnetic Hard Drives
- Use a Data Archiving Service
The way we archive data is constantly changing and evolving. As new technology is developed,data lifecycle management is simplified and enhanced.
Here are some of the best ways to archive data in 2023:
1. Multi-Cloud Storage
Many organizations are turning to the cloud to ensure your data is safe and secure.
Thanks to the development of new technology, such as object-based storage and serverless computing, organizations can now store their data across multiple clouds rather than relying on a single provider.
This is necessary for any organization that values data protection and efficiency.
For example, businesses can use public cloud storage for cost-effective temporary storage and then shift to using hybrid cloud storage for data they value and need long-term retention and protection.
This way, they can avoid any single point of failure that could lead to a potentially catastrophic data loss.
2. Create Your Own Data Lake
A data lake is a centrally located pool of data that any employee can access for any analysis or investigation.
The size of your data lake will depend on your specific needs, but make sure you have a comfortable and accessible space for staff to work.
To create your data lake, you must consider several factors, such as how much space you have and what type of environment you want to keep within your office.
Does your office have a nice view of the park?
Would you like to keep the space cozy and inviting?
What about having a beer machine? It would be best to ask these questions to determine the perfect layout for your ideal data lake.
3. Cloud Archiving Services
Moving data to the cloud can be a complex process that requires expertise you only sometimes have in-house.
Fortunately, there are specialized companies that provide cloud migration services that can move your data to the right platform, ensuring it is stored safely and securely.
For example, if you’re using Office 365 and your cloud provider decides to terminate your service, you can purchase a Cloud Migration Service to move your data to another provider.
This service, which usually entails a one-time fee, will transfer your email, contacts, documents, and settings to a new account or website while you continue using Office 365.
This is a convenient way to ensure your data is always accessible and you’re not left stranded without a cloud service.
The use of data archiving tools and the cloud is a complementary practice that ensures organizations can retain access to their data even if their original cloud provider goes out of business or becomes unreliable.
This, in turn, can help companies to avoid any data lock-in.
4. Tape Archiving
While the cloud is widely used to archive data, it isn’t the only option.
Another more traditional method is to use tape. Various companies provide archiving solutions based on tape.
In addition, tape is cheaper and more robust than hard drives, making it a popular choice among larger organizations.
The upside of using tape for data archiving is that it’s a familiar and well-established technology.
It’s highly compatible with existing file systems and platforms.
This ensures you can continue to use the files you’ve already accumulated without needing to rewrite your systems to use a different technology.
The downside of tape is the physical handling.
Tapes tend to be bulky and, consequently, more difficult to transport and store.
For academic use, mainly, this can be a major obstacle.
In addition, since they’re generally shipped through the mail, they can also be slow and unreliable.
That being said, for many organizations, the tape is still the most practical and cost-effective storage medium.
5. On-site Backups
There’s also the option of storing your data locally and onsite.
This is the most traditional and cost-effective method. Companies such as BackBlaze and Storj provide onsite storage that is completely free.
While this may sound appealing, onsite data storage comes with its own set of challenges.
Most notably, your entire organization needs to be able to access and use the equipment effectively and efficiently.
This requires training and possibly ongoing support from IT personnel.
The advantages of onsite data storage are that it allows you to continue to use your existing equipment and infrastructure.
In addition, you don’t need to worry about servers or connectivity since everything is available directly on your premises.
This ensures you can always access your data when you need it.
It also reduces the space you need to rent since you can store all your files on a single device.
The downside of onsite storage is that it’s vulnerable to natural disasters and theft.
For example, if your data is stored directly onsite, there’s no protection from floods or fires.
Theft is also a significant issue, considering the information many organizations keep on their premises.
6. Network Storage
A more recent development to archive data in the world is network storage.
With the rise of the cloud, it’s not surprising that businesses and organizations have turned to this traditional method of storing data.
The network allows you to access your data anywhere and on any device.
Since it’s digital, it’s always available and can be backed up remotely.
The convenience of this approach is hard to overstate.
Allowing you to access your data from anywhere and any device frees up storage space, ensuring you always have access to your files, even if you don’t have immediate plans to use them.
It also reduces the amount of equipment you need to store.
The downside to the network is that it’s not as secure as some of the alternatives.
If you use consumer-level equipment for storing and accessing your data, there’s a chance it could be compromised.
Hackers often target consumer-level devices due to their unsophisticated security protocols.
If you’re concerned about security, use a dedicated network and encrypt all traffic.
7. Optical Disk Archiving
Another solution that’s been around for a while but continues to hold its own as a reliable and practical alternative to archive data is the optical disk.
The CD, DVD, and Blu-Ray are all based on the same technology and compatible with most existing computing platforms and systems.
This makes optical disk a quick and easy solution to archive data.
The downside to optical disk archiving is that it’s a bit more expensive than magnet tape and the cloud.
This is mainly because optical disks require more sophisticated reading and writing equipment.
But you shouldn’t consider this method if you are looking for a cost-effective and easier data archiving solution.
8. Magnetic Hard Drives
Another alternative to archive data is magnetic hard drives.
These drives are quite a bit more expensive than the other solutions mentioned but offer excellent value for the money.
The advantage of using a hard drive for data archiving is that it provides excellent value for the money.
The downside is that it’s more challenging to transport and move around if you need to archive data than other solutions.
Therefore, it may not be the most practical solution if you need to archive data for a more extended period or if you need to move it frequently to different locations.
However, many organizations still find hard drive archiving the most practical solution.
9. Use a Data Archiving Service
When it comes to archiving data, several different options are available.
However, not all of these options are created equal.
To ensure that your data is adequately archived and protected, you should consider using a data archiving service.
There are many benefits to using a data archiving service.
First, you can be sure that your data will be properly backed up and stored.
Additionally, a data archiving service can help you save money on storage costs by compressing your data to take up less space.
Finally, a data archiving service can provide peace of mind knowing that your data is safe and secure.
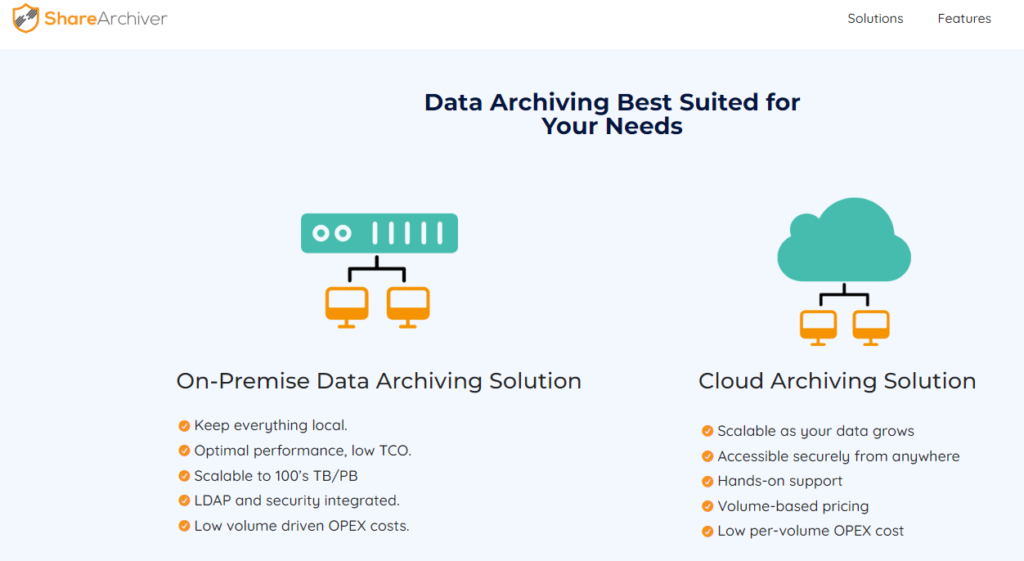
ShareArchiver can provide secure data storage using network security tools, on-prem or cloud storage and back-end file encryption.
In addition, with seamless stubbing capability, you can access archived files repeatedly without interruption.
When choosing a data archiving service, select one like ShareArchiver, which offers online and offline storage options.
This way, you can be sure that your data will be accessible no matter what happens.
Wrapping Up
This article reviews the best ways to archive data in 2023.
While the above solutions cover the main methods used for archiving data, more is needed to choose a data archival solution based on the size of your archive.
Other factors, such as how often you’ll need access to the data and your overall business strategy, should also be considered when making a decision.
If you find that you’ll need to access your data often, there may be better options than the cloud.
If you need a more stable and longer life span, tape drive or hard drives may be your best bet. Ultimately, it depends on your needs.